KLIFS Frequently Asked Questions
How can I cite KLIFS in a publication?
First of all, thank you for using KLIFS and for citing us!
If possible, please cite the latest NAR paper (primary reference) and the reference that matches best with the elements of KLIFS that you have used for your publication. Below is a short summary for each of the papers.
• Primary reference: Nucleic Acids Research paper (database issue of 2021)
Everything regarding the KLIFS website, the web services, and/or data/annotations from the KLIFS database.
• Trends in Pharmacological Sciences (2019)
Everything regarding atypical protein kinases or the comparison between eukaryotic and atypical protein kinases.
• ACS Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (2017)
When using the KNIME nodes for KLIFS.
• Nucleic Acids Research paper (database issue of 2016)
First introduction of the KLIFS website & database. Specific elements: kinase-ligand interactions, G-rich loop/p-loop annotations, water clusters, and quality scoring.
• ACS Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2014)
Everything regarding the initial KLIFS dataset, the binding mode classification, or the residue nomenclature.
Is KLIFS free to use?
Yes, both for academia and industry all data in KLIFS is freely available/open! Moreover, most KLIFS publications (listed above) are open access.
How can I use KLIFS?
A good place to start with KLIFS is via the KLIFS video tutorials in the YouTube channel.
What software and data sources are being used to create KLIFS?
We are using an in-house developed pipeline that combines many different software packages and multiple databases, but the heart of KLIFS has been built using MOE from the Chemical Computing Group analyzing structural data from the Protein Data Bank.
The 3D viewer does not seem to work.
The 3D-viewers (NGL and iview) are WebGL viewers. This means that these viewers do not require the installation of any plugins as all up-to-date modern browsers support WebGL (more information). However, sometimes the configuration of the browser has to be adjusted. Please follow the steps described here to enable webGL for your specific browser.
How did you define the binding site?
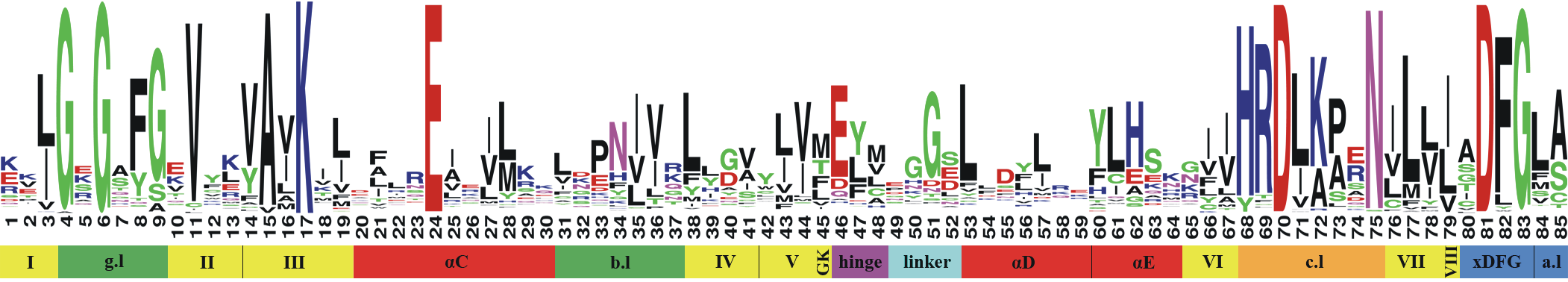
Based on our initial analysis of over 1200 kinase-ligand crystal structures we defined a pocket that comprises 85 residues and covers the interactions between inhibitors and the proteins of type-I, I½, II, III inhibitors and most type IV inhibitors as well. See the image below (and our publication) for more information.
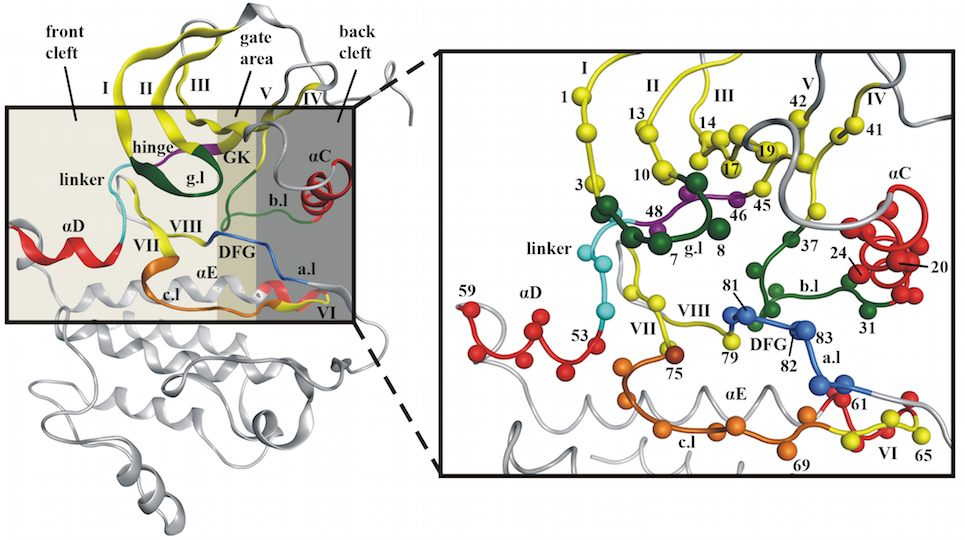
What do all the colors for the residues mean?
Each color represents a specific part of the kinase binding site (e.g. the hinge region is colored magenta, a-helices are colored red, B-sheets are colored yellow, the gatekeeper is colored gold). See the image below (and our publication) for more information.
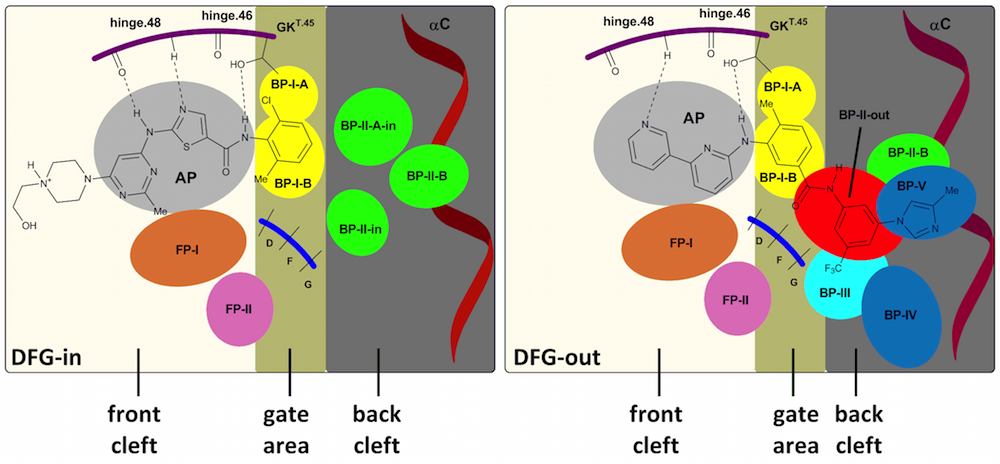
What are these different (sub)pockets?
The binding site of the catalytic domain of kinases can be roughly divided into three main pockets: the front pocket, the gate area and the back pocket. Several kinases also have specific subpockets that have been classified into front pockets I and II, back pockets I-V. A schematic representation is given below (see our publication for more information):
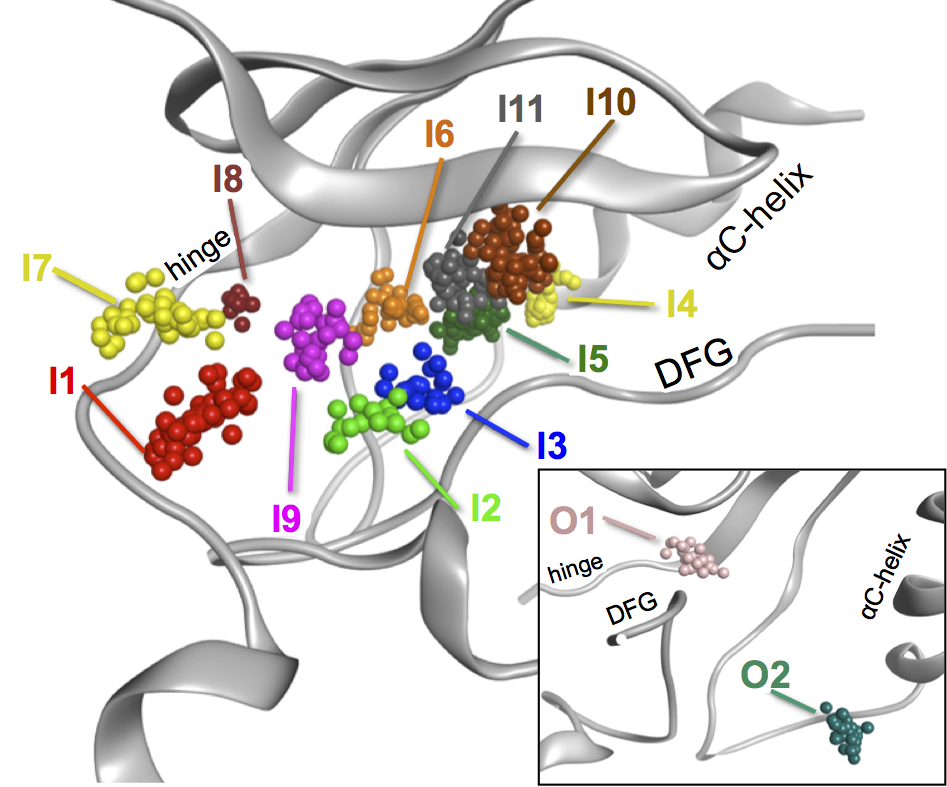
Conserved waters or pocket waters: what do these names like I1, O2 mean?
Based on the overlay of all kinase structure we have analyzed the presence of (highly) conserved waters that frequently interact with the co-crystallized ligand. This resulted in the identification of 13 positions in which water appear in kinase structures with a high frequency. These positions have been named I1-I11 and the DFG-out specific structures have been classified as O1 and O2.The position of these water clusters are highlighted in the figure below:
What is an MOE database?
MOE stands for Molecular Operating Environment and is a fully integrated drug discovery software package of the Chemical Computing Group. The MOE database download processes all the selected structures into a single fully annotated database file for this software package. See their website for more information: Chemical Computing Group
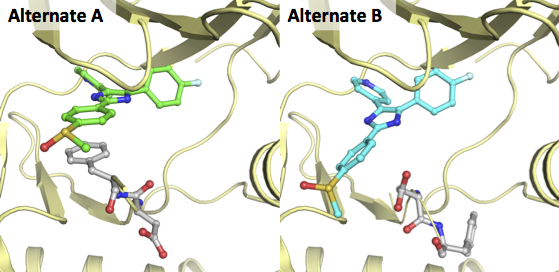
What are these alternates/alternate models?
Alternates are alternative conformations or rotamers that can be defined for a single residue/substance/ligand in a crystal structure. A crystallographer can define alternates when the electron density for these elements are not concentrated on a single spot, but are clearly present on 2 or more spots. Each of the models will then be stored in an alternate (A, B, etc.). However, most PDB-viewer only load the first (A) model discards the rest of this information. As this information can be valuable we have chosen to split the alternates and store them in separate mol2 files.
A great example of two alternates for a ligand and residues is the X-ray of MAP kinase p38 in complex with a pyridinylimidazole (PDB-code 2EWA). In the figure below this structure is depicted for both alternates in exactly the same orientation:
How can I download (all) processed structures from KLIFS?
Where can I download the master sequence alignment?
The master sequence alignment has been optimized for the correct alignment of the 85 pocket residues. This alignment is therefore not suitable to be applied in a different setting. However, for a good overall alignment of kinases, we recommend using the kinase alignment of Manning et al., which is freely available at kinase.com.
I cannot find a specific crystal structure in KLIFS that is present in the PDB, what happened and can you add it?
Please make sure that the PDB structure contains a human or mouse kinase (these are the major species with crystallized kinase domains, others will follow in the future). Please send us the information regarding this structure and we will make sure to add the structure and check why it was not present in KLIFS already (click on the contact button at the bottom).
Can I combine different search options with each other?
Yes, all search options that are shown can be combined. So it is possible to search for an inhibitor that, for example, shares similarity with Dasatinib, belongs to the Ack family, targets the backpocket I B, contains a conserved water at cluster i5, contains a Leucine at the GK+2 position (residue 47) and has an H-bond interaction with the gatekeeper with a minimal crystal structure resolution of 2.5.
I have identified an error (e.g. in the annotation, alignment, atom typing of a structure), can you correct it?
Please send us all information regarding the error using the feedback button at the bottom of the webpage for this specific structure and we will correct it as soon as possible (or you can use the feedback button at the bottom of this page).
Can you please add a specific analysis or feature to your database/website?
Please contact us with your ideas for the improvement of KLIFS (click on the contact button at the bottom).